What is the emf frequency f – Delving into the realm of electromagnetic frequency (EMF), this comprehensive guide unravels the mysteries of EMF frequency f, its potential health effects, and its diverse applications across industries. Prepare to embark on a journey that illuminates the science behind EMF and empowers you with knowledge to navigate its complexities.
EMF frequency f, measured in hertz (Hz), plays a pivotal role in our technological landscape, from powering our smartphones to enabling medical imaging. Understanding its characteristics and implications is crucial for informed decision-making and responsible use of technology.
Definition of EMF Frequency
Electromagnetic frequency (EMF) is a measure of the rate at which an electromagnetic field oscillates. It is expressed in hertz (Hz), which is the number of oscillations per second. The EMF of a field is determined by the speed of the electromagnetic waves and the wavelength of the waves.
Measurement of EMF
The EMF of an electromagnetic field can be measured using an EMF meter. EMF meters measure the strength of the electric and magnetic fields present in an environment. The measurements are typically expressed in milligauss (mG) or volts per meter (V/m).
Types of EMF Frequency Ranges: What Is The Emf Frequency F

EMF frequencies are categorized into various ranges, each with its own characteristics and sources.
Extremely Low Frequency (ELF)
- Range: 0-300 Hz
- Examples: Power lines, household appliances
Intermediate Frequency (IF)
- Range: 300 Hz – 30 MHz
- Examples: AM radio, shortwave radio
Radio Frequency (RF)
- Range: 30 MHz – 300 GHz
- Examples: Cell phones, Wi-Fi routers, microwaves
Extremely High Frequency (EHF)
- Range: 300 GHz – 30 THz
- Examples: Millimeter waves, imaging systems
Health Effects of EMF Frequency
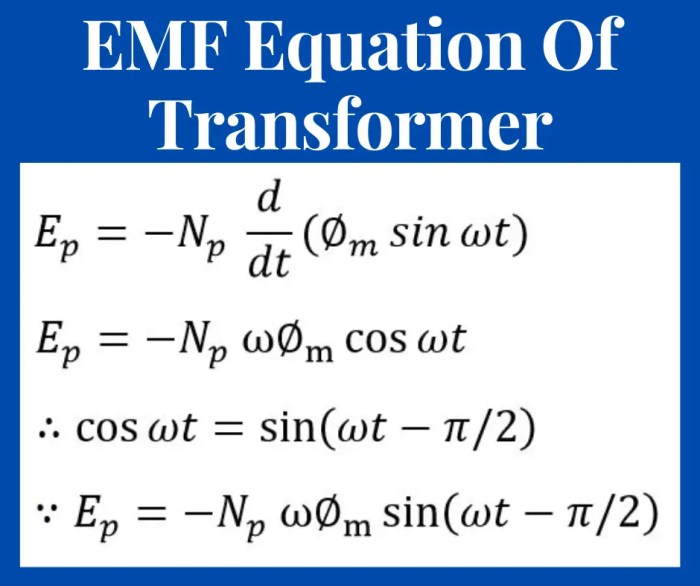
Exposure to different EMF frequencies has been a topic of concern due to potential health effects. The evidence and controversies surrounding these effects vary depending on the frequency range and the specific health outcomes being studied.
Some studies have suggested that exposure to low-frequency EMF, such as those emitted by power lines and electrical appliances, may be associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer, particularly childhood leukemia. However, the evidence for this association is still considered inconclusive, and more research is needed to establish a causal relationship.
Exposure to high-frequency EMF, such as those emitted by cell phones and wireless devices, has also been investigated for potential health effects. Some concerns have been raised about the possible link between cell phone use and brain tumors, but the evidence to date is inconclusive.
The emf frequency f is a measure of the number of times the electric field oscillates per second. The root poli appears in various words related to government and society, such as politics , policy , and police . Interestingly, the emf frequency f can also be influenced by political decisions and policies, as these can affect the allocation of resources and the implementation of regulations related to electromagnetic fields.
Further research is needed to determine whether there is a causal relationship between cell phone use and any specific health outcomes.
EMF Frequency Measurement and Mitigation
To ensure optimal health and safety, it is crucial to measure and mitigate exposure to potentially harmful EMF frequencies. Understanding the methods for measuring EMF frequencies and implementing practical mitigation strategies empowers individuals to take control of their exposure levels.
EMF Frequency Measurement
Various methods are available for measuring EMF frequencies, each with its advantages and limitations:
- Gauss Meter:Measures magnetic field strength, commonly used for assessing exposure from electrical appliances and power lines.
- Radio Frequency Meter:Detects and measures radiofrequency (RF) emissions from wireless devices and base stations.
- Electrosmog Detector:Comprehensive device that measures both electric and magnetic field strengths, providing a holistic assessment of EMF exposure.
EMF Frequency Mitigation
Reducing exposure to harmful EMF frequencies can be achieved through practical measures:
- Distance:Maintain a safe distance from EMF sources, such as power lines and wireless routers.
- Shielding:Use EMF-shielding materials, such as conductive fabrics or paints, to block or reduce EMF emissions.
- Grounding:Connect electrical devices to the ground to dissipate EMF energy.
- Reduce Wireless Usage:Limit the use of wireless devices and connect to wired networks whenever possible.
Applications of EMF Frequency
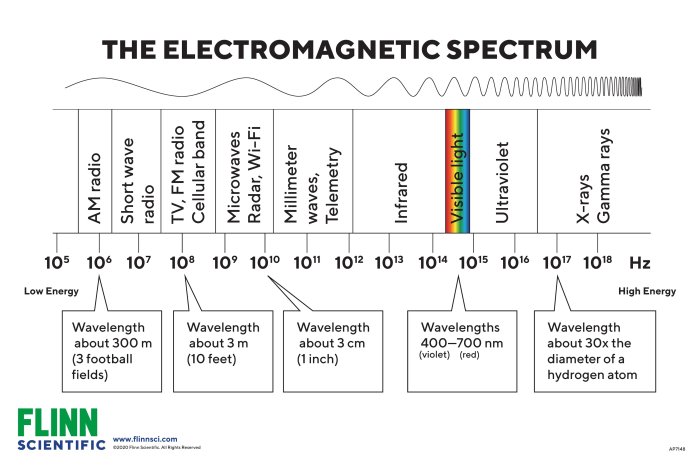
Electromagnetic frequency (EMF) finds applications across diverse industries and technologies, spanning from communication to healthcare. The specific frequency range employed depends on the intended purpose, each offering unique benefits and challenges.
Communication
- Radio waves:Used for broadcasting, mobile communication, and wireless networks, enabling long-range communication and data transmission.
- Microwaves:Utilized in satellite communication, radar systems, and microwave ovens, providing high-speed data transfer and precise object detection.
Medical Imaging
- X-rays:Generate images of internal structures, aiding in diagnosing and treating medical conditions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):Employs strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of tissues and organs, assisting in medical diagnosis and research.
Industrial Processes, What is the emf frequency f
- Microwave heating:Used in food processing, drying, and industrial heating applications, providing efficient and rapid heating.
- Induction heating:Employed in metalworking and manufacturing, enabling precise and controlled heating of conductive materials.
Benefits and Challenges
EMF frequencies offer numerous advantages, including efficient communication, medical advancements, and industrial efficiency. However, potential challenges associated with certain frequency ranges, such as exposure to high levels of radiation, must be carefully considered and managed to ensure safety.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between EMF and ionizing radiation?
EMF is non-ionizing radiation, meaning it does not have enough energy to remove electrons from atoms. Ionizing radiation, such as X-rays and gamma rays, has higher energy and can cause damage to DNA and cells.
What are the potential health effects of EMF exposure?
Research on the health effects of EMF is ongoing, but some studies have suggested a possible link between long-term exposure to high levels of EMF and certain health conditions, such as cancer and reproductive problems. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
How can I reduce my exposure to EMF?
There are several ways to reduce your exposure to EMF, including using a wired headset instead of a wireless one, limiting the use of electronic devices before bed, and maintaining a distance from high-voltage power lines.
