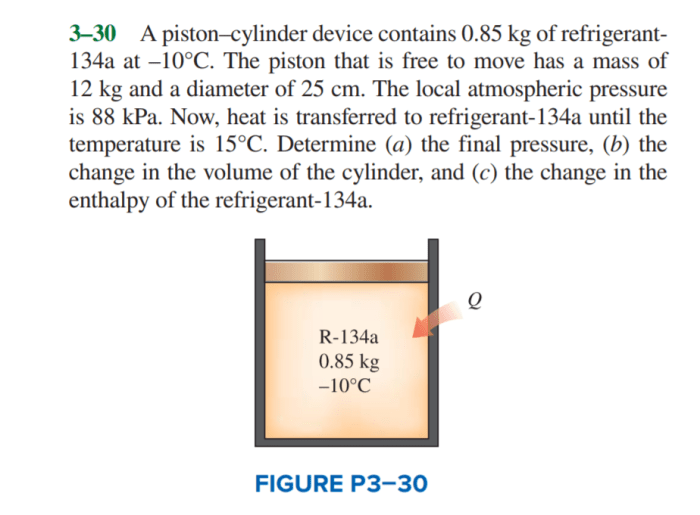
A piston cylinder device contains 0.85kg of refrigerant – A piston cylinder device containing 0.85kg of refrigerant presents a fascinating subject for exploration within the realm of thermodynamics. These devices play a pivotal role in various refrigeration and air conditioning systems, and their understanding is crucial for optimizing their performance and efficiency.
The significance of the refrigerant mass in piston cylinder devices stems from its direct influence on the thermodynamic processes that occur within the system. The amount of refrigerant present affects the pressure, volume, and temperature relationships, ultimately impacting the device’s overall performance and efficiency.
By delving into the thermodynamic properties of refrigerants and their impact on piston cylinder devices, we gain valuable insights into the behavior and optimization of these systems.
1. Introduction

Piston cylinder devices are widely used in various thermodynamic applications. They consist of a cylinder and a movable piston that compresses or expands a working fluid, typically a refrigerant. These devices play a crucial role in refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pump systems.
2. Thermodynamic Properties of Refrigerant
Refrigerants are substances used in piston cylinder devices that undergo phase changes to absorb and release heat. Their thermodynamic properties, such as pressure, temperature, and specific volume, are essential for analyzing the performance of these devices. Common refrigerants include hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), and natural refrigerants like ammonia and carbon dioxide.
3. Mass of Refrigerant
The mass of refrigerant in a piston cylinder device directly affects its performance. A higher mass of refrigerant increases the system’s capacity to absorb and release heat. However, it also increases the pressure and temperature within the device, which can impact its efficiency and longevity.
4. Pressure-Volume (P-V) Diagram
A P-V diagram is a graphical representation of the pressure and volume changes of the refrigerant in a piston cylinder device. It provides insights into the thermodynamic processes occurring within the device. To create a P-V diagram, data from experimental measurements or theoretical calculations are plotted on a graph, with pressure on the y-axis and volume on the x-axis.
5. Thermodynamic Processes, A piston cylinder device contains 0.85kg of refrigerant
Various thermodynamic processes occur in piston cylinder devices, including isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, and isochoric processes. These processes affect the pressure, volume, and temperature of the refrigerant and determine the overall performance of the device.
6. Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a fundamental aspect of piston cylinder devices. Heat can be transferred into or out of the device through conduction, convection, or radiation. Understanding heat transfer principles is crucial for optimizing the efficiency and performance of these devices.
7. Efficiency Analysis
Efficiency is a key parameter in evaluating the performance of piston cylinder devices. Various methods are used to analyze the efficiency, including the coefficient of performance (COP) and thermal efficiency. These metrics provide insights into the device’s ability to convert energy and produce cooling or heating effects.
8. Applications
Piston cylinder devices have numerous applications in real-world systems. They are commonly used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to provide cooling and temperature control. Additionally, they are employed in heat pumps for heating and cooling purposes. These devices offer advantages such as high efficiency, reliability, and versatility.
Popular Questions: A Piston Cylinder Device Contains 0.85kg Of Refrigerant
What is the purpose of a piston cylinder device?
A piston cylinder device is a mechanical system that utilizes a piston moving within a cylinder to compress or expand a fluid, typically a refrigerant. This process enables the transfer of heat and work, making these devices essential components in refrigeration, air conditioning, and other thermodynamic applications.
How does the mass of refrigerant affect the performance of a piston cylinder device?
The mass of refrigerant in a piston cylinder device directly influences the pressure-volume relationships and thermodynamic processes occurring within the system. A higher refrigerant mass generally leads to higher pressures and temperatures during compression and lower pressures and temperatures during expansion, impacting the device’s efficiency and performance.