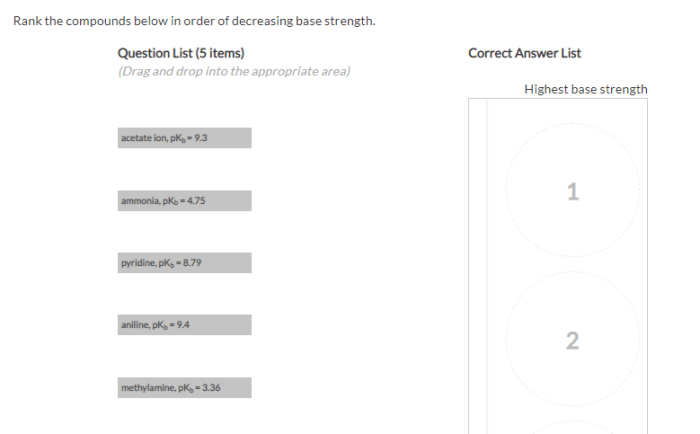
Rank the compounds below in order of decreasing base strength – Delving into the intricacies of base strength ranking, this exploration unravels the factors that govern the relative strength of compounds as bases. By understanding the principles behind this ranking system, we gain valuable insights into predicting reaction outcomes, designing new materials, and comprehending biological processes.
Factors such as molecular structure, electron-withdrawing or donating groups, and nitrogen atom hybridization play a crucial role in determining base strength. Various methods, including pKa values, acid-base equilibrium constants, and the Hammett acidity function, provide valuable tools for ranking compounds based on their decreasing base strength.
Introduction
Base strength is a measure of the ability of a compound to accept protons. It is an important property in chemistry as it affects the reactivity of compounds in acid-base reactions. Ranking compounds based on decreasing base strength allows us to predict their behavior in various chemical processes.
Factors Affecting Base Strength

The base strength of a compound is influenced by several factors, including:
- Molecular structure:The presence of electron-withdrawing or donating groups can affect the basicity of a compound. Electron-withdrawing groups decrease base strength, while electron-donating groups increase base strength.
- Hybridization of the nitrogen atom:Nitrogen atoms in sp 2hybridization are more basic than those in sp 3hybridization.
Methods for Ranking Compounds

There are several methods used to rank compounds based on decreasing base strength, including:
- pKa values:The pKa value of a compound is a measure of its acidity. The lower the pKa value, the stronger the base.
- Acid-base equilibrium constants:The equilibrium constant for an acid-base reaction can be used to determine the relative base strength of the reactants.
- Hammett acidity function:The Hammett acidity function is a measure of the acidity of a solution. It can be used to compare the base strength of compounds in different solvents.
Applications of Base Strength Ranking: Rank The Compounds Below In Order Of Decreasing Base Strength
Ranking compounds based on decreasing base strength has several practical applications, including:
- Predicting reaction outcomes:The base strength of reactants can be used to predict the products of acid-base reactions.
- Designing new materials:The base strength of materials can be used to design materials with specific properties.
- Understanding biological processes:The base strength of biomolecules can be used to understand their function in biological systems.
Examples and Case Studies
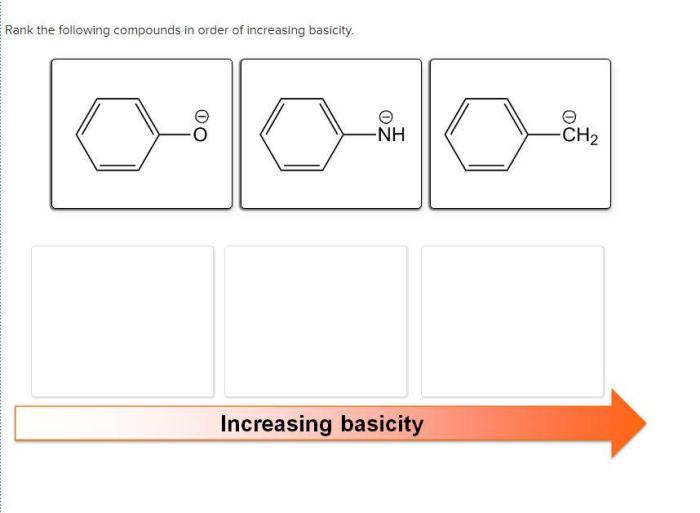
Here are some examples of how base strength ranking is used in practice:
- Amine basicity:Amines are a class of organic compounds that are basic. The basicity of amines can be ranked using pKa values. The more basic the amine, the lower its pKa value.
- Buffer solutions:Buffer solutions are solutions that resist changes in pH. The base strength of the weak acid and weak base used to prepare a buffer solution determines its buffering capacity.
Limitations and Considerations
There are some limitations and considerations associated with ranking compounds based on decreasing base strength:
- Solvent effects:The base strength of a compound can be affected by the solvent in which it is dissolved.
- Temperature:The base strength of a compound can also be affected by temperature.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of ranking compounds based on decreasing base strength?
Ranking compounds based on decreasing base strength provides valuable insights into their chemical reactivity, enabling the prediction of reaction outcomes, design of new materials, and understanding of biological processes.
How do factors such as molecular structure and hybridization influence base strength?
Molecular structure, including the presence of electron-withdrawing or donating groups, and the hybridization of the nitrogen atom significantly impact base strength. Electron-withdrawing groups decrease base strength, while electron-donating groups enhance it. Hybridization also plays a role, with sp2-hybridized nitrogen atoms exhibiting greater base strength than sp3-hybridized nitrogen atoms.
What are the limitations of ranking compounds based on decreasing base strength?
While ranking compounds based on decreasing base strength provides valuable insights, it is essential to consider limitations such as solvent effects and temperature. The ranking may vary depending on the solvent used and the temperature at which the measurements are taken.