Population regulation in the Serengeti answers questions about the intricate mechanisms that govern the balance and fluctuations of wildlife populations within this iconic ecosystem. This exploration delves into the interplay of predation, herbivory, resource availability, disease, human activities, and spatial distribution, providing a comprehensive understanding of the factors shaping the Serengeti’s diverse wildlife communities.
As we embark on this journey, we uncover the dynamic relationships between predators and herbivores, the delicate balance between resource availability and population size, and the profound influence of human activities on the Serengeti’s ecological tapestry.
Population Regulation in the Serengeti
Population regulation is a complex process that influences the size and dynamics of populations within an ecosystem. In the Serengeti ecosystem, a variety of factors interact to regulate the populations of its diverse wildlife species.
Population Dynamics in the Serengeti
Population regulation involves the mechanisms that maintain the stability of populations within an ecosystem. These mechanisms can be either density-dependent or density-independent.
Density-Dependent Factors
- Competition for resources:When population density is high, individuals compete for limited resources such as food, water, and shelter, which can limit population growth.
- Predation:Predators can significantly reduce prey populations, especially when prey density is high.
- Disease and parasitism:Outbreaks of disease or infestations of parasites can spread rapidly through dense populations, causing mortality and reducing population size.
Density-Independent Factors, Population regulation in the serengeti answers
- Environmental disturbances:Natural events such as droughts, floods, or wildfires can cause large-scale mortality, regardless of population density.
- Climate change:Long-term changes in climate can alter the availability of resources and habitat, impacting population dynamics.
Predation and Herbivory
Predators, such as lions and cheetahs, play a crucial role in regulating herbivore populations in the Serengeti.
Predation
- Prey selection:Predators typically target vulnerable individuals, such as the young, old, or sick, reducing the overall fitness of prey populations.
- Population control:By reducing prey populations, predators prevent overgrazing and maintain a balance between herbivores and vegetation.
Herbivory
- Vegetation impact:Herbivores, such as wildebeest and zebras, consume large quantities of vegetation, shaping the plant communities and influencing ecosystem dynamics.
- Nutrient cycling:Herbivores facilitate nutrient cycling by consuming plants and depositing waste, enriching the soil for other organisms.
Resource Availability
The availability of resources, such as water and food, is a key factor in population regulation.
- Seasonal changes:The Serengeti experiences distinct wet and dry seasons, which influence the availability of water and vegetation, impacting population dynamics.
- Droughts:Prolonged droughts can lead to water scarcity and food shortages, causing population declines and increased mortality.
Disease and Parasitism
Diseases and parasites can significantly impact wildlife populations in the Serengeti.
- Disease outbreaks:Outbreaks of diseases, such as rinderpest and anthrax, can spread rapidly through dense populations, causing mass mortality.
- Parasite infestations:Parasites, such as ticks and fleas, can weaken individuals, reduce reproductive success, and increase susceptibility to disease.
Human Activities
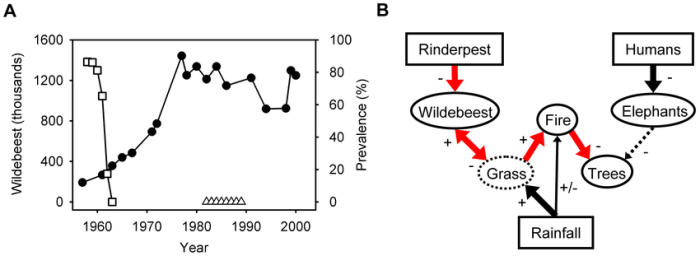
Human activities can have a profound impact on population regulation in the Serengeti.
- Hunting:Illegal hunting can deplete populations and disrupt predator-prey relationships.
- Habitat fragmentation:Human settlements and infrastructure can fragment habitats, reducing connectivity and limiting access to resources.
- Conservation efforts:Conservation measures, such as protected areas and anti-poaching initiatives, can contribute to maintaining healthy wildlife populations.
Spatial Distribution
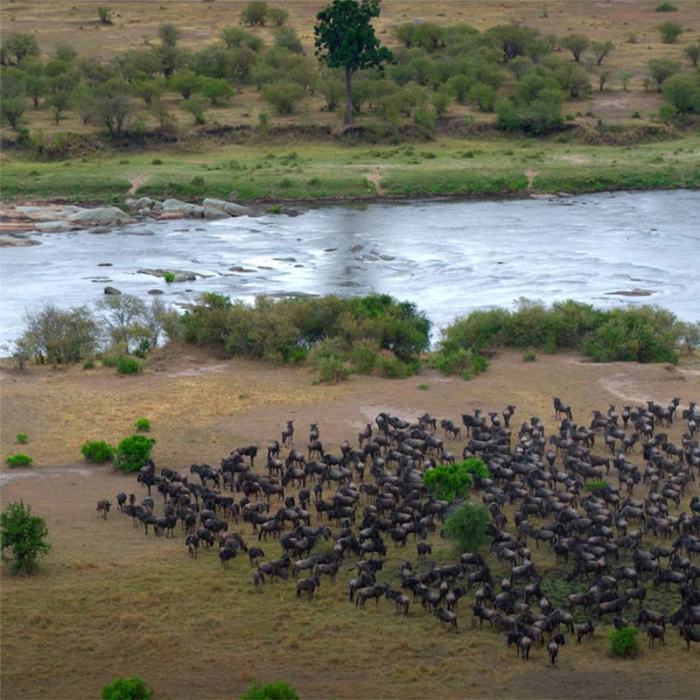

The spatial distribution of wildlife populations in the Serengeti is influenced by various factors.
- Habitat preferences:Different species have specific habitat preferences, such as open grasslands, woodlands, or wetlands, which determine their distribution.
- Resource availability:The availability of water, food, and shelter influences the distribution of populations within their habitats.
Population Monitoring and Management: Population Regulation In The Serengeti Answers

Monitoring wildlife populations is crucial for effective management and conservation.
- Monitoring techniques:Various techniques are used to monitor populations, including aerial surveys, camera traps, and telemetry.
- Data analysis:Population data is analyzed to assess population trends, identify threats, and inform conservation strategies.
Helpful Answers
What are the primary density-dependent factors influencing population size in the Serengeti?
Competition for resources, predation, and disease outbreaks.
How do seasonal changes affect population dynamics in the Serengeti?
Seasonal droughts can limit resource availability, leading to population declines, particularly among herbivores.
What role do humans play in population regulation within the Serengeti?
Human activities such as hunting and habitat fragmentation can disrupt natural population dynamics and impact species interactions.