The poh of pure water at 40c is 6.8 – The pOH of pure water at 40°C is 6.8, a fundamental concept in water chemistry that reveals the delicate balance of water’s properties. This value holds profound significance in understanding water quality and its behavior in various applications.
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the pOH of water. As temperature increases, the ionization of water molecules intensifies, leading to a higher concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). This shift in ion concentrations directly affects the pOH of water.
pH of Pure Water
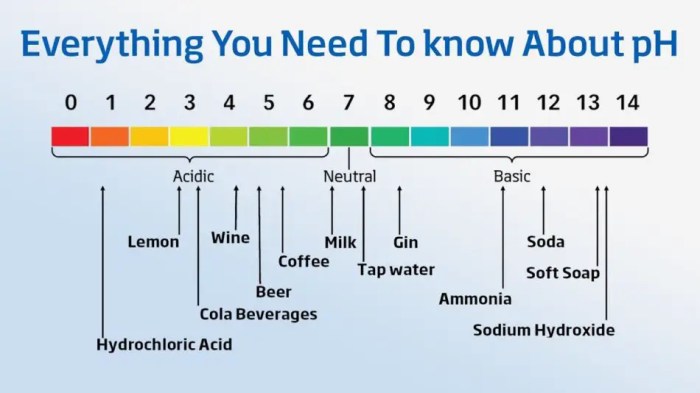
The pH of a substance is a measure of its acidity or basicity. It is expressed on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH value less than 7 indicates acidity, while a pH value greater than 7 indicates basicity.
The pH of pure water is 7 at 25°C, which means that it is neutral. However, the pH of pure water can change with temperature.
Temperature and pH of Pure Water
The pH of pure water decreases with increasing temperature. This is because the water molecules become more energetic at higher temperatures, and they are more likely to break apart into hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions causes the pH of the water to decrease.
At 40°C, the pH of pure water is 6.8. This means that the water is slightly acidic. The decrease in pH from 7 to 6.8 is due to the increased concentration of hydrogen ions in the water.
Ionization of Water

Water is a unique substance that has the ability to ionize, meaning that it can break apart into positively and negatively charged ions. This process is essential for many biological and chemical reactions, and it is also what gives water its slightly acidic pH.
The ionization of water occurs when a water molecule (H 2O) loses a hydrogen ion (H +) and becomes a hydroxide ion (OH –). This process is reversible, and the equilibrium constant for the reaction is 1.0 x 10 -14at 25°C.
Kw= [H +][OH –] = 1.0 x 10 -14
The concentration of hydrogen ions in water is inversely proportional to the pH of the water. This means that as the pH of water increases, the concentration of hydrogen ions decreases, and vice versa.
Impact of Temperature on the Ionization of Water
The ionization of water is affected by temperature. As the temperature of water increases, the equilibrium constant for the ionization reaction also increases. This means that at higher temperatures, there are more hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in water.
For example, at 40°C, the equilibrium constant for the ionization of water is 2.9 x 10 -14. This means that at 40°C, the concentration of hydrogen ions in water is approximately 1.7 x 10 -7M, which is higher than the concentration of hydrogen ions in water at 25°C.
pH Measurement Techniques

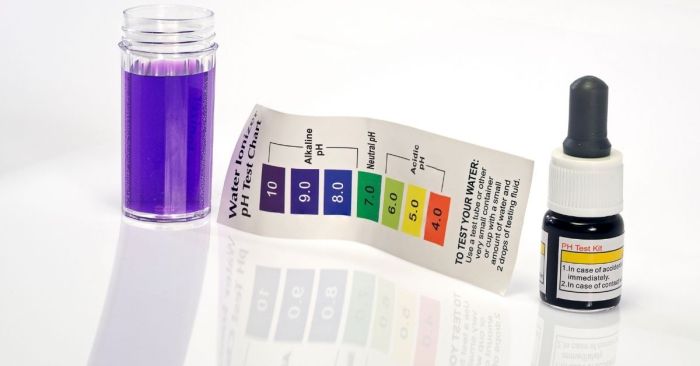
The pH of a solution can be measured using various techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include colorimetric indicators, pH meters, and electrodes.
Colorimetric Indicators
Colorimetric indicators are substances that change color depending on the pH of the solution. They are typically used in the form of litmus paper or universal indicator solution. Litmus paper is a simple and inexpensive way to measure pH, but it is not very accurate.
Universal indicator solution is more accurate than litmus paper, but it can be more difficult to interpret the results.
pH Meters, The poh of pure water at 40c is 6.8
pH meters are electronic devices that measure the pH of a solution by measuring the electrical potential difference between a glass electrode and a reference electrode. pH meters are more accurate than colorimetric indicators, but they are also more expensive.
pH meters can be used to measure the pH of a wide range of solutions, including pure water.
Electrodes
Electrodes can also be used to measure the pH of a solution. Electrodes are typically made of glass or metal, and they are coated with a pH-sensitive material. When the electrode is placed in a solution, the pH-sensitive material reacts with the hydrogen ions in the solution, and the electrical potential of the electrode changes.
The electrical potential of the electrode can be used to determine the pH of the solution.
Measuring the pH of Pure Water at 40°C Using a pH Meter
To measure the pH of pure water at 40°C using a pH meter, follow these steps:
- Calibrate the pH meter according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Rinse the pH electrode with distilled water.
- Immerse the pH electrode in the pure water sample.
- Wait for the pH reading to stabilize.
- Record the pH reading.
Applications of pH in Water Treatment: The Poh Of Pure Water At 40c Is 6.8

pH plays a crucial role in water treatment processes, influencing the efficiency of various treatment steps, including coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection. Understanding the optimal pH range for each process is essential to ensure effective water treatment and meet regulatory standards.
Coagulation
Coagulation is the process of destabilizing suspended particles in water, causing them to clump together and form larger particles. The optimal pH range for coagulation depends on the type of coagulant used. For example, alum, a commonly used coagulant, works best at a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
Flocculation
Flocculation is the process of promoting the growth of coagulated particles, allowing them to settle more rapidly. The optimal pH range for flocculation is typically slightly higher than that for coagulation, ranging from 6.5 to 7.5. At this pH range, the particles are less likely to redisperse and can be more easily removed from the water.
Disinfection
Disinfection is the process of killing or inactivating microorganisms in water. The effectiveness of disinfection depends on the pH of the water. For example, chlorine, a widely used disinfectant, is most effective at a pH range of 6.5 to 7.5. At higher pH levels, chlorine becomes less effective due to the formation of hypochlorite ions.
By adjusting the pH of water, water treatment plants can optimize the efficiency of these processes, improve water quality, and meet regulatory standards for drinking water.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of pOH in water quality?
pOH is a measure of the alkalinity or acidity of water, indicating the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-). It plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of water treatment processes and the suitability of water for various uses.
How does temperature affect the pOH of water?
Temperature influences the ionization of water molecules, altering the concentration of H+ and OH- ions. As temperature increases, the ionization increases, resulting in a higher concentration of ions and a lower pOH.
What is the optimal pH range for water treatment?
The optimal pH range for water treatment varies depending on the specific application. For coagulation and flocculation, a pH range of 6.5-7.5 is generally preferred, while disinfection processes may require a higher pH.